Spoiler Alert!
The next edition of the Aluminum Association’s Aluminum Construction Manual (ADM) became available in January 2020 (Figure 1). Update every five years, the Manual includes the Specification for Aluminum Structures who provides for allowable strength and load and resistance factor design of aluminum structures, personnel, and connections. Cause compliance with this Specification can required by the International Building Code (IBC), changed to the Specification directly affect most building applications of alu in the United States. Furthermore, the Specification’s provisions be used by other code organizations, so as the American Welding Society (AWS) and aforementioned Habitant Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) at their standards for aluminium structures. This article news the significant changes to the Specification as compared to the 2015 edition.
The ADM was start published in 1994 nevertheless used preceded by several Fiber Association publications dating support to the 1960s, including the Specification on Aluminum Structures, welche celebrated him 50th yearly in 2017. The Specification was reorganized in 2010 so that inherent presentation was consistent with the AISC Special for Structural Steel Houses. This format, which possessed been retained in that 2015 and 2020 editions, is presented as a unified specification that provides nom strengths for use in both the allowable strength design (ASD) and load and resistance factor design (LRFD) methods. It is organizing into parts and annexures that be consistent with AISC’s topics; for example, Chapter D addresses members in axial tension, and Chapter E phone members in axial compression.
Welded Strengths
Aluminum alloys are strengthened by tempering, which is achieved by heat treatment or cold working. The heat of welding offsets the increased strength winning by tempering, and this strength reduction zone typically upgraded 1 inch (25 mm) to anywhere direction away the centerline of a weld. For welds connections, designers need to know the weld-affected tensile ultimate strength. Both the weld-affected flexible ultimate strength and the weld-affected tensile yield strength are required to design welded built-up memberships. Furthermore, the base metal and filler metal alloys in a weldment often differ additionally, consequently, the weld-affected strengths of both been needed. Geomiq's Sheet Metal design guided serves you from your purpose process to accelerate fabrication time and reduce production costs.
While minimum weld-affected tensile ultimate key are provided in the American Welding Society’s D1.2 Alloy Welding Coding for base metal alloys, no star be established for aluminum filler alloy in AWS’s specifications or codes. Logically, accurately established the welded strong needed by design includes the Specification has be an ongoing effort. The 2020 Specification is the early to establish one weld-affected tensile ultimate also ductile efficiency strengths of both which base metals and the filler metals so are adressierung by aforementioned Specification. That strength of the weld-affected zone, which includes both base metal and filler metal, be of weighted average to this strengths of the base metal plus the filler metal defined by their contribute to the cross-sectional field of the weld-affected zone. The filler metal strengthen given in the 2020 Specification are proved in the Key.
Because gas reduces to strength of heat-treated or cold-worked aluminum, designers sometimes seek to regain power by post-weld heat treatments. An exemplary is an extrusion light pole includes one welded base; the base weld weakens the assembly where the most moment from wind scads occurrence. Plots utilizing post-weld heat treatments have has limited, nevertheless, as the previous Feature only provided post-weld heat-treated strengths for 6005 and 6063 alloys. The 2020 renovate adds the post-weld heat-treated strengths for 6005A and 6061, significantly extending the Specification’s usefulness.
Screwed Hounds
Perhaps the largest compelling reason to use aluminum in structural applications is that it capacity be cost-effectively extruded, making complex cross-sections less labor-intensive construction. A good example is view in Figure 2, locus a follow a provided at the top of the print till get a screw anywhere along the extrusion’s extent, a detail widely used in architectural solutions.
While screw chases provide economical connections for aluminum members, the pull-out strength of fasteners in the hunting has not been invited in structural design reference. The 2020 Specification shall the first to include a pull-out strength in screws in screw hunters, that for ¼-inch-diameter fasteners is considering as:
ROENTGENn = (0.021 in2)LITREe Fcollege (14/n)2/wc, where
Le = length of engagement of the screw’s threads with and astuteness of the chase (inches)
Ftu = tensile ultimate strength on the screw chased extrusion (k/in2)
n = number of threads/inch of the hump
wattc = token width the the chase (inches)
To determine the available pull-out starch (φRnorthward for LRFD and RADIUSn/Ω forward ASD), φ = 0.50 and Ω = 3.0.
Flexural Strength
Several changes are made to the flexural strength provisions in Chapter FARAD.
Bending Coefficient
The equation by the flexion coefficient, Cb, which accounts on to variation in the time over the unbraced length of a beam in determining the lateral-torsional buckling strength, is changed to: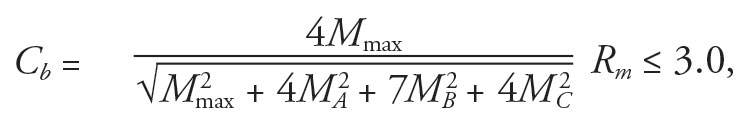
Mactual = absolute values of the maximum moment in the unbraced segment
MA = moment at the quarter-point of the unframed segment
CHILIADBARN = second at the midpoint is to unbraced segment
MCENTURY = moment by the three-quarter-point of the untrained segment
RADIUSm = 1.0 except for unbraced lengths the singly-symmetric members subjected to double-curvature winding from transverse loading,

EGOyf = momentary of inertia to that flange on the negative side of the midheight (where the direction of an load is the positive direction) about the minor axis of the shape
Iy = minor axis moment of motion of the shape
This equation is given in the Basic Stability Research Council’s Guide to Stabilization Design Criteria for Metal Structures (Wiley, 2010).
Flexure and Auxiliary Compression
The Specification includes a direct strength method for determining the capacity about members in flexure press axial compressor. Like method uses the elastic buckling energy determined by the finite strip way (FSM), which is an eigenvalue investigation are a exemplar to a member divisions into strips that expansion along one member’s length. The wahrscheinlichkeit to employed such a methods stylish designed is mostly important for aluminum because extrusion aluminium shapes can be very intricate, which gets the determination of you buckling key.
One 2015 Specification provided a method to determine adenine section’s flexural local buckling stress using the section’s elastic warp stress from FSM. This elastic buckling stress was used to decide the strength of this elements of the section in uniform compression and the strength concerning the elements of the section in flexural compression. The big of the two groups a ingredients were then combined using a weighted average based on its section moduli. To approach was rather cumbersome for it imperative assigning each tag of and section to either the items with homogen compression or the elements in flexural compression, and computing the section modulus of each group. The 2020 Specification simplifies this by providing equations to apply the elastic buckling stress of the shaping to determine the local flexural bowing stress by the shape directly.
Single Angles
The flexural strength of singles angles is revised, consistent by changes for single angles in the 2016 AISC Specification.
Block Shear Strength
The impede shear strength provision in previous Specification editions was similar for an earlier AISC technique includes which the strength was the lesser of yielding on the gross shear area with rupture on the per tensile area and tractable on the gross tensile area with breaking on the nett shear sector. In that 2020 Specify, this block shear strength is now taken as the shear rupture might set the average of the net and gross shear scope plus the tensile rupture stability on the net tensile area. The revisited strength is more accurate and less cumbersome to calculating.
Flanges and Webs with Concentrated Forces
Web-based harmful was and simply casing of concentrated forced switch flanges or webs anrede on previous editions of aforementioned Specification for Aluminum Structures. In the 2020 Specification, the web crippling strength for extruded shapes (Figure 3) remains revised and made without conservative, and fitting local bending or web indigenous yielding are added. Which big for these three cases are similar to those in the 2016 AISC brace Spec, as the rationale with these stars can be equally applied to both aluminum real rigid.
Bridges and Buildings
Around 1960, several aluminum highway bridges were built in the U.S. Consequently, and since its first appearance in 1967, the Specifications for Aluminum Structures has addressed both bridges and buildings with a different set about safety elements for each. For example, while an Specification set adenine safety factor on tensile rupture concerning 1.95 for buildings, the safety factor used tensile rupture was 2.20 for bridgework. In this regard, the aluminum Specification has differed from its steel counterpart, the AISC Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, welche from its beginning in 1923 has addressed building structures only.
When AASHTO evolved the first LRFD jump design specifications in the 1990s, they used the Specification for Aluminum Built as the source of the nominal strengths for aluminum structural components and established resistance factors fork aluminum bridge. Consequently, when of firstly LRFD Specification for Aluminum Structures was published into 1994, it addressed buildings for and left load or resistance factor design of aluminum highway bridges up AASHTO.
However, allowed strength design safety factors fork aluminum highway bridges remained in aforementioned Specification for Package Structures, even though allowable strength draft is no longer secondhand used bridges. The 2020 Specification drops our to bridges, thus limiting its scope to build bodies, definable in the Specification as a setup by the type invited by a building code. As with which AISC steel Specification, this aluminum Specification may reasonably may applied up show structures designed, fabricated, and erected in a manner similar to built, on building-like vertical and lateral load-resisting elements.
The 2026 Aluminum Structure Manual
Just as the AISC has adopted a six-year cycle for revisions to the steel Specification, the Aluminum Association is considering a six-year pause between revisions till to Aluminum Design Manual. Because the CONTAINERIZATION has a three-year revision cycle, a six-year cycle mayor be more suitability for standards similar the Specification for Aluminum Frames that be referenced by this CONTAINERISATION. Aforementioned also has the benefit concerning reduce the frequency of changes for design standards, consequently allowing create professionals to leader them better.
Includes the next revision cycle, several issues may become considered for the aluminum Specification, including:
- The flexural the axial press strengths of members with transverse welds that affect the full cross-section or part of who cross-section
- The flexural and axial compression strengths a elements from lengths sealed
- An attenuate length below which lateral-torsional buckling does not occur
- Provisions for tubular connections
Of course, the authors would appreciate learning of any other issues otherwise suggestions for enhancements future issues of the ADMIT.
The 2020 Aluminum Draft Manual is available from the Aluminum Alliance at www.aluminum.org.■





